DONANEMAB
- Home
- DONANEMAB
What is donanemab?
Donanemab is a monoclonal antibody developed by Eli Lilly that removes a protein called beta-amyloid from the brain. It is infused through a vein for about 30 minutes monthly for 18 months.
Patients with Alzheimer’s disease have a build-up of the proteins, beta-amyloid and tau in their brain. The accumulation of these proteins is thought to result in the degeneration of neurons and the associated cognitive decline. With the help of your immune system, donanemmab selectively targets and removes the beta-amyloid from the brain.
Donanemab Phase 3 Trial: TRAILBLAZER ALZ2
Donanemab slows cognitive decline in patients with Alzheimer’s disease
Commentary
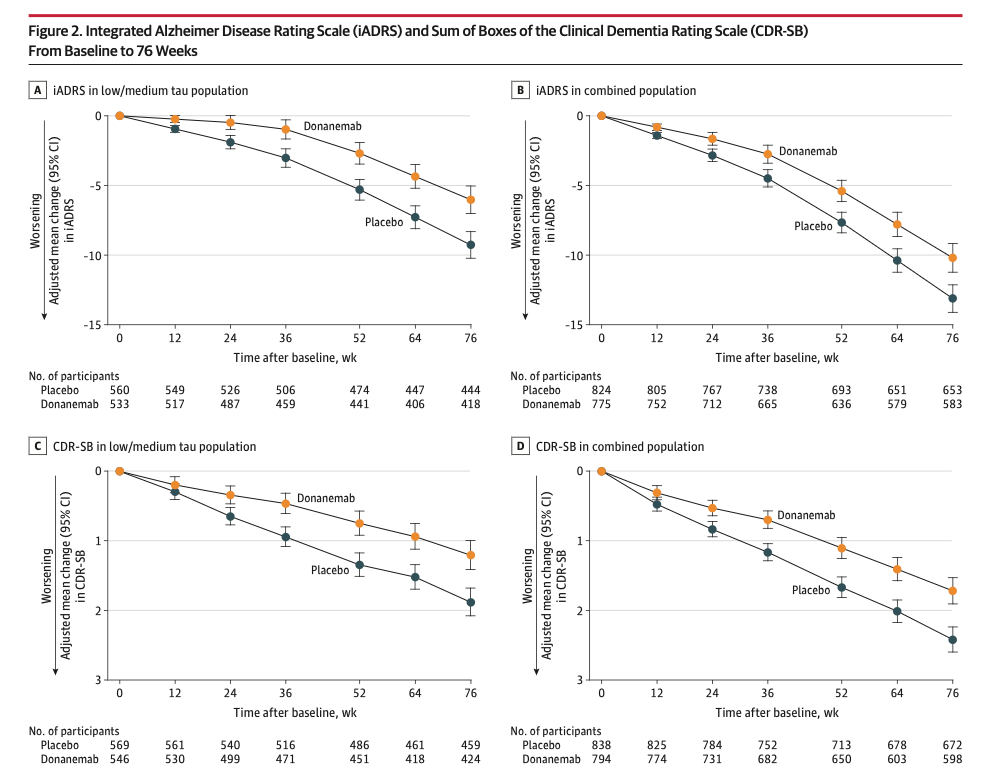
Donanemab slows cognitive decline (as detected by the iADRS) and activities of daily living (as detected by the CDR-SB) over the course of 76 weeks by about 30%. The Trailblazer-ALZ2 study also measured the amount of tau through a Tau-PET scan as an independent marker of disease severity, with high levels of tau considered more severe disease.
Donanemab was even more effective in patients with less advanced disease, defined as those with low/medium tau.
Donanemab removes amyloid and possibly tau from the brain
Commentary
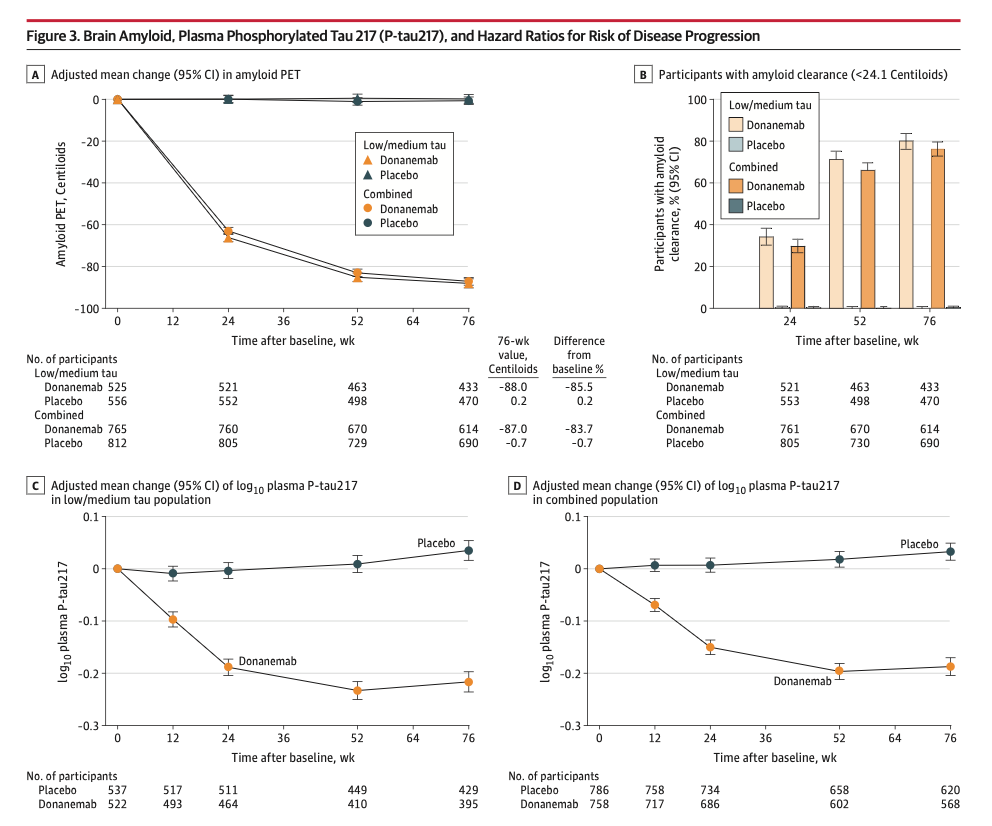
There is no evidence that those patients with the most amyloid removed had the most benefit clinically. We do not know the significance of the amyloid removal.
Donanemab was STOPPED in patients when they no longer had evidence of amyloid in the brain. These patients continued to show benefit of the donanemab treatment throughout the entire treatment period.
Over the course of the study donanemab reduced tau levels (p-tau 217) in the blood, but did not affect the amount of tau in the brain as detected by Tau-PET scan.
Which patients benefit the most from donanemab?
Commentary
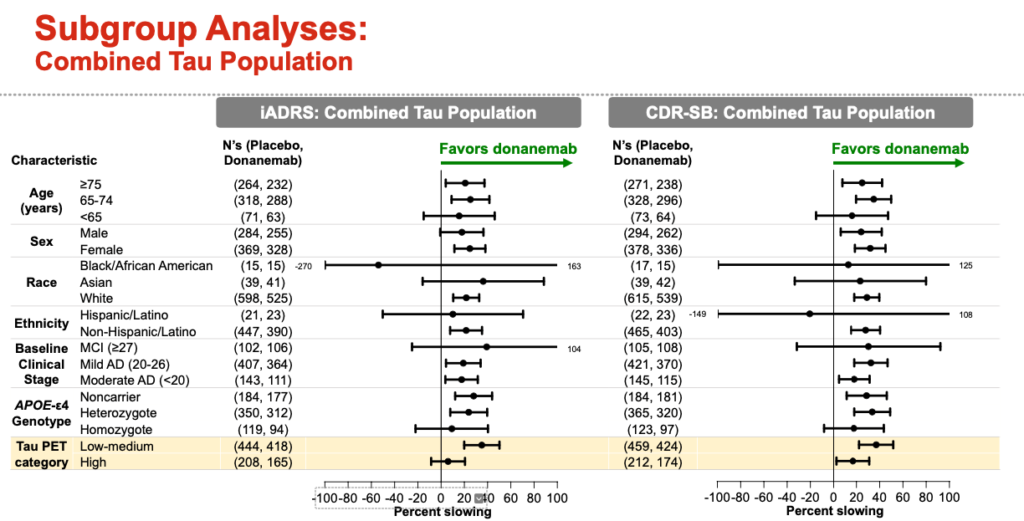
ApoE4 noncarriers, patients with low tau burden responded better to donanemab.
Conversely ApoE4/E4 (Homozygote) carriers and patients with high tau burden did not respond as well to donanemab.
African Americans/Blacks and Hispanics had a highly variable response to donanemab because of the low number of patients.
Adverse Events
Commentary
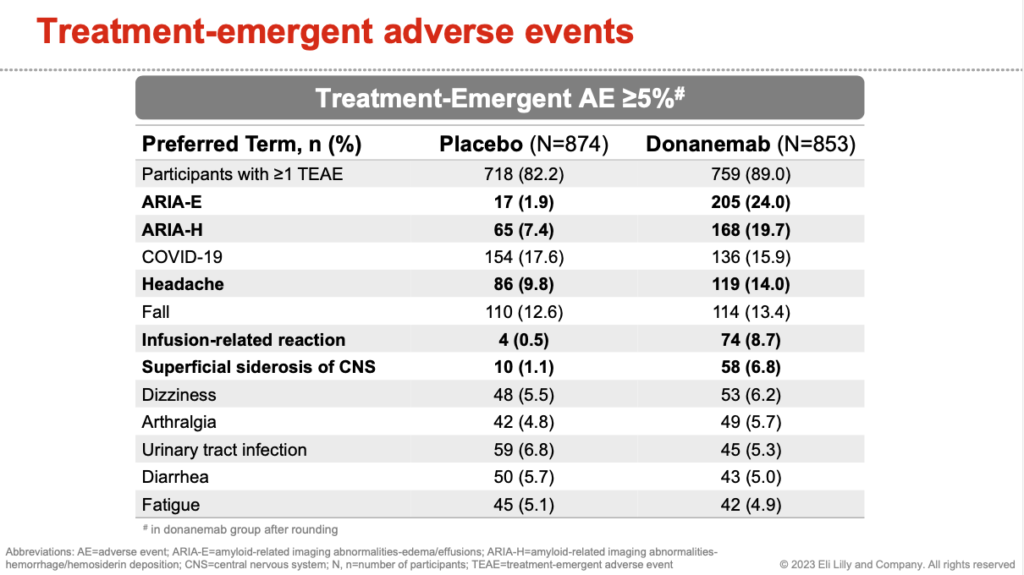
The most concerning side effect was ARIA – Amyloid Related Imaging Abnormalities. This is either swelling (ARIA-E) or bleeding (ARIA-H) in the brain.
24% of patients receiving donanemab will develop ARIA-E and 6% will have symptomatic ARIA-E requiring stopping donanemab. Symptoms include headaches, visual problems, and confusion.
8.7% of patients will have an infusion related reaction and 4% were moderate to severe. 3 patients (0.4%) had a serious reaction. There were no deaths related to infusion reactions.
There was 1 fatality from brain bleeding in a patient who was on donanemab.
There were 2 fatalities from brain swelling and edema in patients who received donanemab.
FAQ
What is the difference between lecanemab and donanemab?
Both lecanemab and donanemab are monoclonal antibodies directed against amyloid and work similarly.
Lecanemab is infused every 2 weeks while donanemab is infused monthly. After 18 months, lecanemab will switch to monthly subcutaneous injections (done at home). Donanemab infusions are continued until the patients’ amyloid-PET scan becomes negative.
Benefits are similar with both slowing decline by about 30%
Major risk for both medications being infusion related reactions and ARIA. Donanemab has about 1/2 risk for infusion reactions and double the risk for ARIA.
Is donanemab currently available?
Donanemab has been approved by the FDA and the BIDMC DiAD will be offering donanemab to our eligible patients in the Fall of 2024.
